
5 Those at higher risk for severe illness should be prioritized for vaccination. Additionally, those of all ages with underlying medical conditions, including but not limited to heart disease, diabetes or lung disease, are at higher risk to develop severe COVID-19 compared to those without these conditions. The risk of severe disease increases steadily as people age. 5 These severe complications often lead to death. In some cases, people who get COVID-19 can develop severe complications, including difficulty breathing, causing a need for hospitalization and intensive care. People at Higher Risk for Severe IllnessĬOVID-19 is a relatively new disease therefore, additional risk factors for severe COVID-19 may continue to be identified. It is important to note that some people become infected and do not develop any symptoms or feel ill. The estimated incubation period is between 2 and 14 days with a median of 5 days. Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.SymptomsĪ wide range of symptoms for COVID-19 have been reported. 2,3 Other factors that are associated with increased COVID-19 risk include prolonged exposure to those infected with COVID-19, close contact with infected persons, and any other activity that leads to exposure to a greater amount of respiratory droplets and particles. In indoor spaces with poor ventilation, the concentration of virus particles is often higher than outdoors. There are certain circumstances that can increase the risk of infection for COVID-19 such as poorly ventilated space. Additionally, transmission can occur from those with mild symptoms or from those who do not feel ill. Respiratory droplets can land on hands, objects, or surfaces around the person when they cough or talk, and people can then become infected with COVID-19 from touching hands, objects or surfaces with droplets and then touching their eyes, nose, or mouth. A physical distance of at least 1 meter (3 ft) between persons is recommended by the WHO to avoid infection, 1 whereas CDC recommends maintaining a physical distance of at least 1.8 meters (6ft) between persons. Infectious droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby or possibly be inhaled into the lungs. The droplets that contain the SARS-CoV-2 virus are released when someone with COVID-19 sneezes, coughs, or talks. By touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with hands that have the SARS-CoV-2 virus particles on them.By having droplets and particles that contain the SARS-CoV-2 virus land on the eyes, nose, or mouth – especially through splashes and sprays like a cough or sneeze.

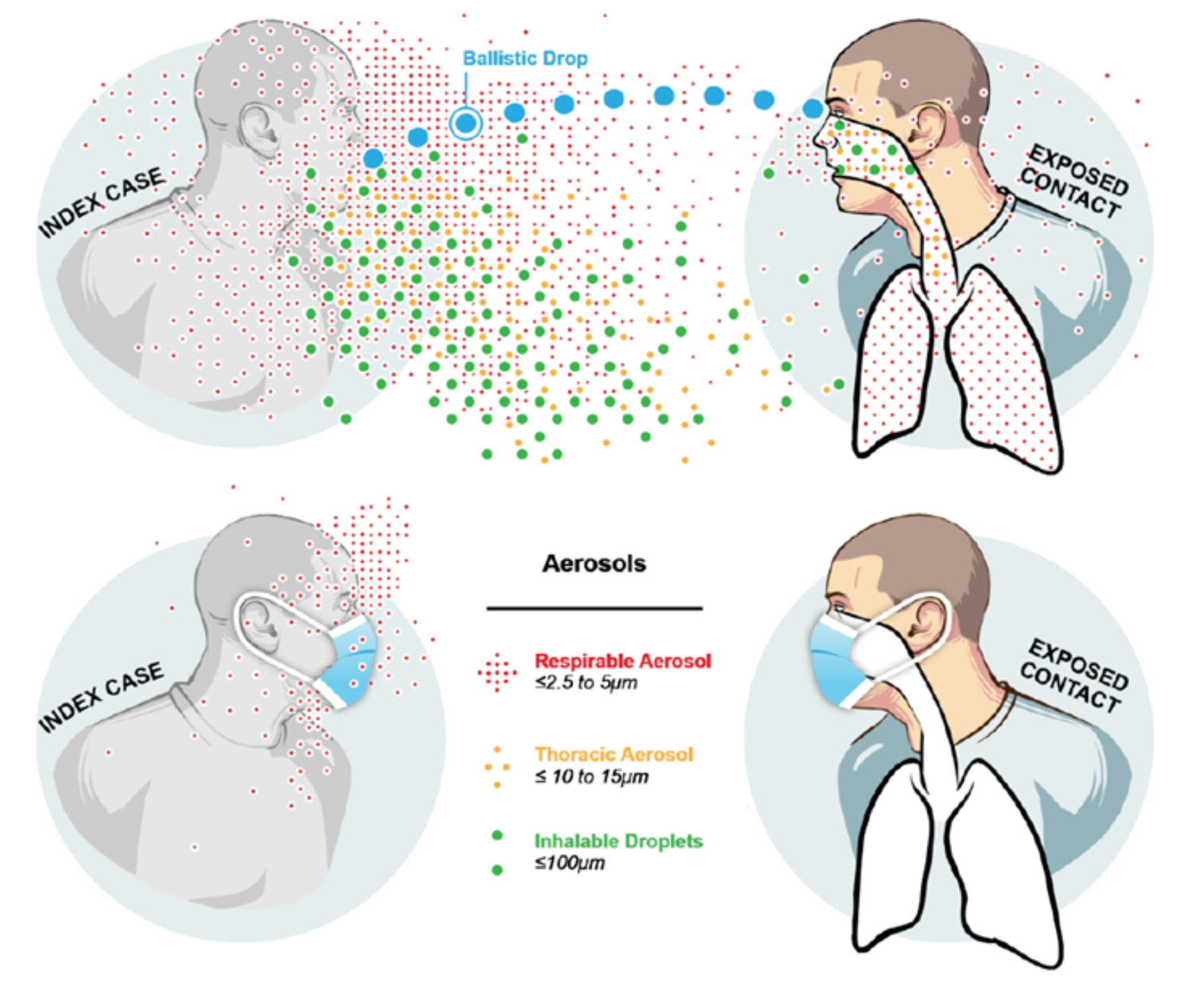
By breathing in air carrying droplets or aerosol particles that contain the SARS-CoV-2 virus when close to an infected person or in poorly ventilated spaces with infected persons.There are three main ways that COVID-19 can spread: Additionally, travel-related exportation of cases occurred. Early in the outbreak, many patients were reported to have a link to a large seafood and live animal market however, later cases with no link to the market confirmed person-to-person transmission of the disease. COVID-19 is caused by the virus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a new virus in humans causing respiratory illness which can be spread from person-to-person. COVID-19 was identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
